2G & 3G closure: Why it’s happening and what it means for your IoT
A big change to mobile networks is occurring as operators across the world gradually migrate from 2G and 3G to more advanced network technologies. Businesses with Internet of Things (IoT) devices which use 2G or 3G as their main source of connectivity, or for back-up connectivity need to be aware of the change and plan for action.
Why are 2G & 3G being phased out?
The change is gradually happening across the world, and a number of countries even have legislation in place which makes the sunsetting of 2G and 3G obligatory. Regardless of whether it’s a legal requirement or not, the explanation for the widespread shift is easy to understand. Doing so frees up spectrum space for high-performing newer technologies like 4G and 5G which not only use that spectrum more efficiently, but are also designed to deliver the more complex, data-heavy services that today’s digital world demands.
Along with the connected device and app economy we have all become used to, these newer technologies enable even further developments in areas like IoT. This includes new advanced use cases ranging from autonomous industry vehicles to automated manufacturing, and much, much more. Innovative IoT business cases are already being deployed and many more will follow thanks to the possibilities unlocked by modern network technologies.
A more detailed explanation of the reasons for the 2G and 3G sunset can be found in the Ericsson, Telia and Transforma Insights 2G and 3G Switch-off white paper.
When and where are older networks being switched off?
The speed of the switch-off varies according to region and country – Japan and South Korea for example already discontinued support for 2G devices as far back as 2011 – but the list of operators around the world who are sunsetting their 2G and 3G networks is long, so make sure you’re aware of the details of the situation in your local market.
In Europe it is common practice to switch off 3G first, as 2G generally has wider coverage for delivering basic voice and data services, while widespread 4G coverage can now cover mobile broadband data demand.
The gradual 3G sunset has started in most of our own markets, with the aim of closing by the end of 2024. For 2G, the ambition is to retire the network by the end of 2025 – but local circumstances will determine the timeline for each country. Specific information can be found on our local websites, telia.se, telia.fi, telia.no, telia.dk, telia.lt, telia.ee
The figure below shows an overview of the various generations of network technologies and how long they are expected to be in use.
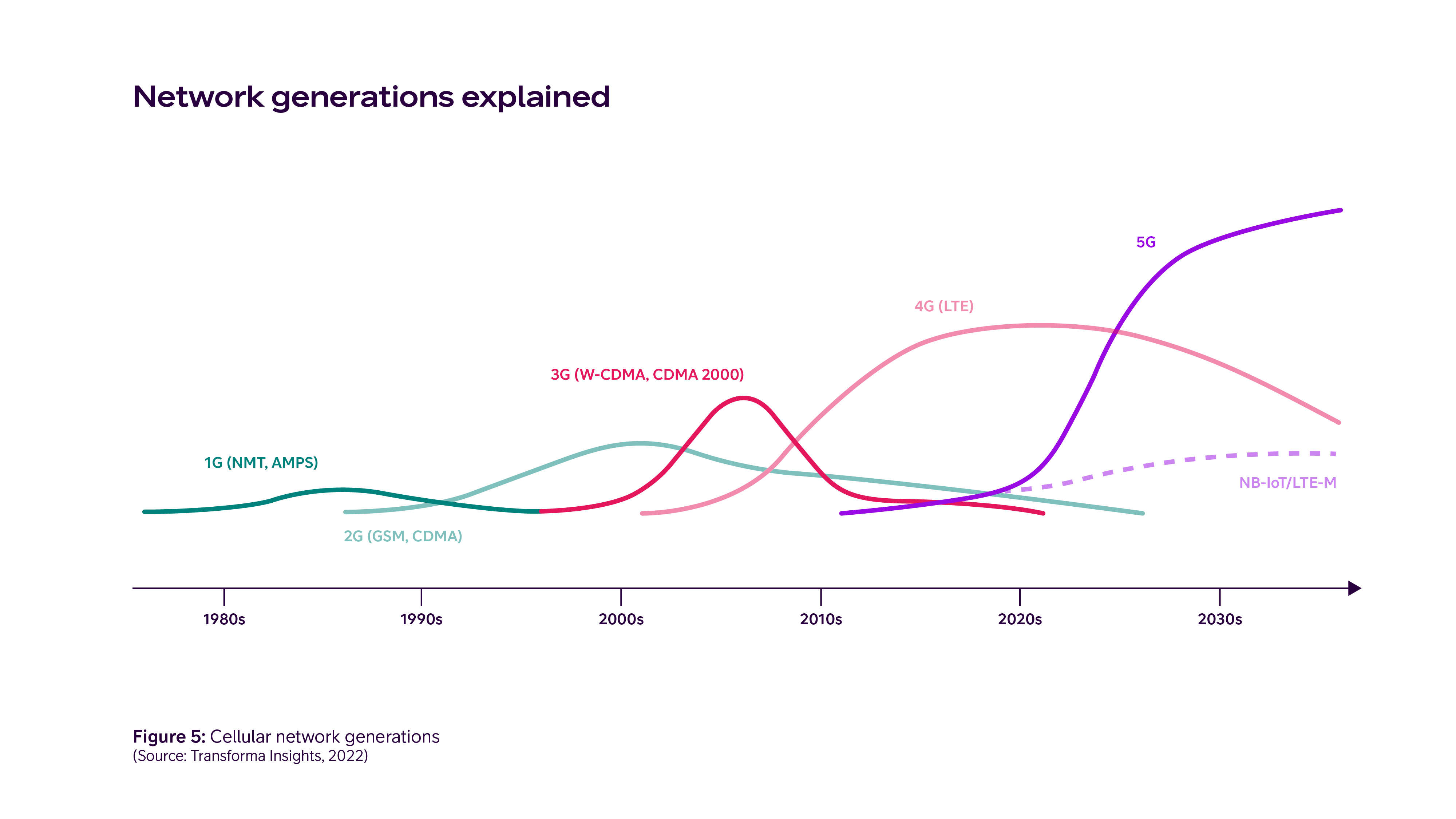
How should I act?
Any business with IoT devices using 2G or 3G connectivity needs to be aware of the details and timeline of the sunset in their local market. Newer devices may already be multi-mode (which means they’re capable of connecting to 4G or other modern network technologies), but older devices will likely need to be replaced before the shutdown occurs, making planning important if they are currently deployed in the field.
Need some help in getting started?
- Our five minute guide to planning that process can be found here
- And our guide to modernizing your IoT, contains a practical list of questions to answer in order to determine the best action to take for your IoT enterprise.
What will it mean?
While the sunset of 2G and 3G does create a need for planning and eventual action, it also creates opportunities for businesses to take advantage of. The shift is ultimately driven by a necessity that exists already today for greater data throughput, better coverage and more efficient power consumption from connectivity solutions.
Technologies like NB-IoT and LTE-M are meeting much of today’s demand on low power and wide coverage while the most modern technology, 5G, comes with a number of new features that unlock a broader range of low latency and highspeed use cases.
As explained in our article on the key business benefits of NB-IoT and LTE-M, switching to these technologies make it possible to improve coverage and deploy IoT devices in a much larger range of locations, while improved battery life means they can be left to operate for longer.
On top of these improvements, 5G features like edge computing bring massive processing power close to IoT devices, clearing a path to roll out much more demanding use cases than previously possible – think autonomous mining vehicles, smart factories and much more. The possibilities for new, innovative IoT solutions are almost endless.
Have you decided to upgrade from 2G or 3G and want to know more about the connectivity options available? Download our white paper, written together with Transforma Insights and Ericsson, where we compare the capabilities of cellular technologies available today.
Cookie notification
Cookies allow us to optimize your use of our website. We also use third-parties cookies for advertising and analytics. Please read our Cookie Policy for more information.

